Relations/Predicates
Predicates are building-blocks in predicate calculus: p(a_1, a_2, …, a_k)
parent(X, Y): X is a parent of Y.
parent(pam, bob).
parent(bob, ann).
parent(tom, bob).
parent(bob, pat).
parent(tom, liz).
parent(pat, jim).
parent(pam, bob).
parent(tom, bob).
parent(tom, liz).
…
male(X): X is a male.
male(tom).
male(bob).
male(jim).
…
female(X): X is a female.
female(pam).
female(pat).
female(ann).
female(liz).
We attach meaning to them, but within the logical system they are simply structural building blocks, with no meaning beyond that provided by explicitly-stated interrelationships
Rules:
mother(X, Y): X is the mother of Y.
In First Order Logic (FOL or predicate calculas):
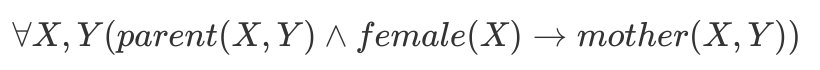
In Prolog:
mother(X, Y) :- parent(X, Y), female(X).
all variables are universally quantified outside the rule
','meansand(conjunction),':-'meansif(implication) and';'meansor(disjunction).
More Relations:
1
2
3grandparent(X, Y) :-
parent(X, Z),
parent(Z, Y).can be read in two ways:
For all X, Y and Z, if X is a parent of Z and Z is a parent of Y, then X is a grandparent of Y.
For all X and Y, X is a grandparent of Y if there is some Z such that X is a parent of Z and Z is a parent of Y.
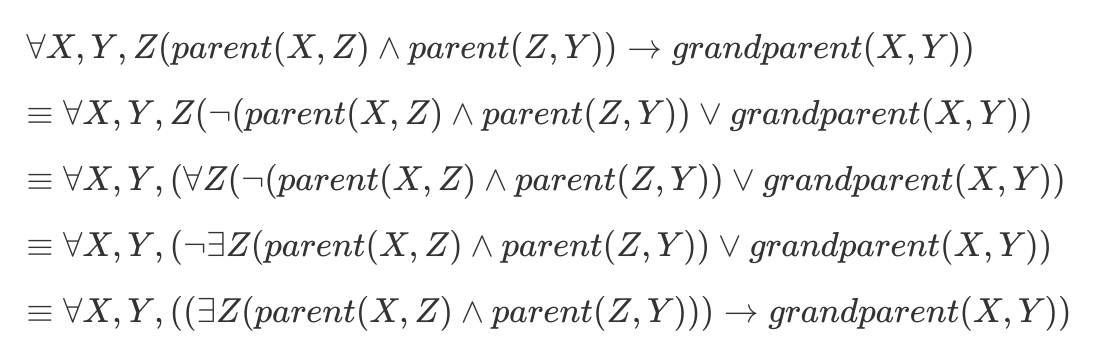
1
2
3
4sibling(X, Y) :-
parent(Z, X),
parent(Z, Y),
X \= Y. % naf safety condition: negation only applies to bound variables1
2
3
4cousin(X, Y):-
parent(A, X),
parent(B, Y),
sibling(A, B).1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9uncle(X, Y) :-
parent(Z, Y),
sibling(X, Z),
male(X).
uncle(X, Y) :-
parent(Z, Y),
sibling(W, Z),
husband(X, W).1
2
3aunt(X, Y):-
uncle(Z, Y),
husband(Z, X).1
2
3
4aunt(X, Y):-
parent(Z, Y),
sibling(X, Z),
female(X).1
greatgrandparent(X, Y):- ...
1
greatgreatgrandparent(X, Y):- ...
Recursion:
1
2
3
4ancestor(X, Y):-
parent(X, Y);
parent(X, Z),
ancestor(Z, Y).INFINITE LOOP
ancestor(X, Y) :- ancestor(X, Z), parent(Z, Y); parent(X, Y).